Introduction
The healthcare landscape has undergone a seismic shift in recent years, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on patient-centric care. One of the most transformative developments is the rise of remote cardiac monitoring, which allows patients to manage heart conditions from the comfort of their homes. This shift from hospital-based to home-based care has been made possible by sophisticated medical devices, but an often-overlooked component plays a critical role in this ecosystem: medical-grade power adapters. These specialized power sources ensure that remote cardiac monitoring devices operate reliably, safely, and efficiently, enabling continuous care outside clinical settings. This article explores the pivotal role of medical-grade power adapters in facilitating remote cardiac monitoring, delving into their technical specifications, regulatory requirements, and impact on patient outcomes.
The Rise of Remote Cardiac Monitoring
Remote cardiac monitoring refers to the use of portable, wearable, or implantable devices to track a patient’s heart activity outside traditional healthcare facilities. These devices, such as electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors, Holter monitors, and implantable loop recorders, collect real-time data on heart rate, rhythm, and other vital parameters. The data is transmitted to healthcare providers via wireless networks, allowing for timely interventions without the need for in-person visits.
The demand for remote cardiac monitoring has surged due to several factors. First, the global prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) continues to rise. According to the World Health Organization, CVDs are the leading cause of death globally, accounting for approximately 17.9 million deaths annually. Early detection and continuous monitoring are critical for managing conditions like arrhythmias, heart failure, and coronary artery disease. Second, the aging population and the increasing burden on healthcare systems have necessitated innovative solutions to reduce hospital admissions and healthcare costs. Remote monitoring addresses these challenges by enabling proactive care and reducing the need for emergency interventions.
However, the success of remote cardiac monitoring hinges on the reliability of the devices used. These devices must operate continuously, often for extended periods, and deliver accurate data to healthcare providers. This is where medical-grade power adapters come into play, serving as the backbone of these systems by ensuring an uninterrupted power supply and compliance with stringent safety standards.
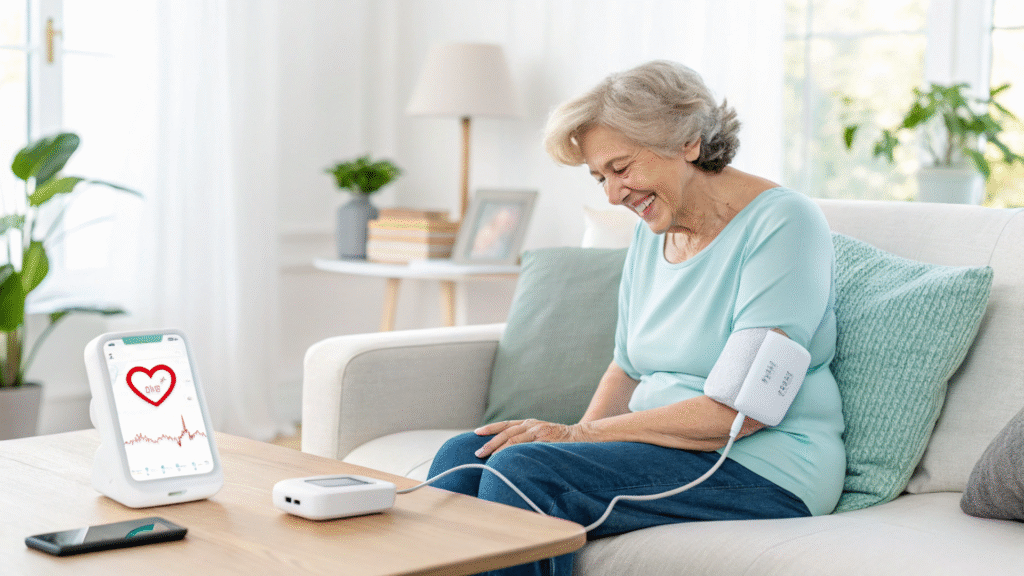

The Role of Medical-Grade Power Adapters
Medical-grade power adapters are specialized power supplies designed to meet the rigorous demands of medical devices. Unlike standard consumer-grade adapters, they are engineered to comply with international safety and performance standards, such as IEC 60601-1, which governs the safety and effectiveness of medical electrical equipment. These adapters provide stable, reliable power to devices, ensuring they function correctly in diverse environments, from hospitals to patients’ homes.
Key Features of Medical-Grade Power Adapters
- Safety and Isolation: Medical-grade power adapters are designed with enhanced electrical isolation to protect patients and operators from electrical shocks. They typically feature double or reinforced insulation and low leakage currents, which are critical for devices that come into direct contact with patients, such as wearable ECG monitors.
- Reliability and Durability: Remote cardiac monitoring devices often operate 24/7, requiring power adapters that can withstand continuous use without overheating or failing. Medical-grade adapters are built with high-quality components to ensure long-term reliability, even in challenging conditions like fluctuating home power grids.
- Compact and Lightweight Design: For home use, power adapters must be portable and unobtrusive. Medical-grade adapters are designed to be compact and lightweight, allowing patients to carry or position them easily without compromising their mobility or comfort.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Medical devices must operate without interference from other electronic devices. Medical-grade power adapters comply with EMC standards (e.g., IEC 60601-1-2) to minimize electromagnetic interference, ensuring accurate data collection and transmission.
- Energy Efficiency: With growing emphasis on sustainability, medical-grade power adapters are designed to meet energy efficiency standards, such as Level VI efficiency requirements, reducing power consumption and environmental impact.
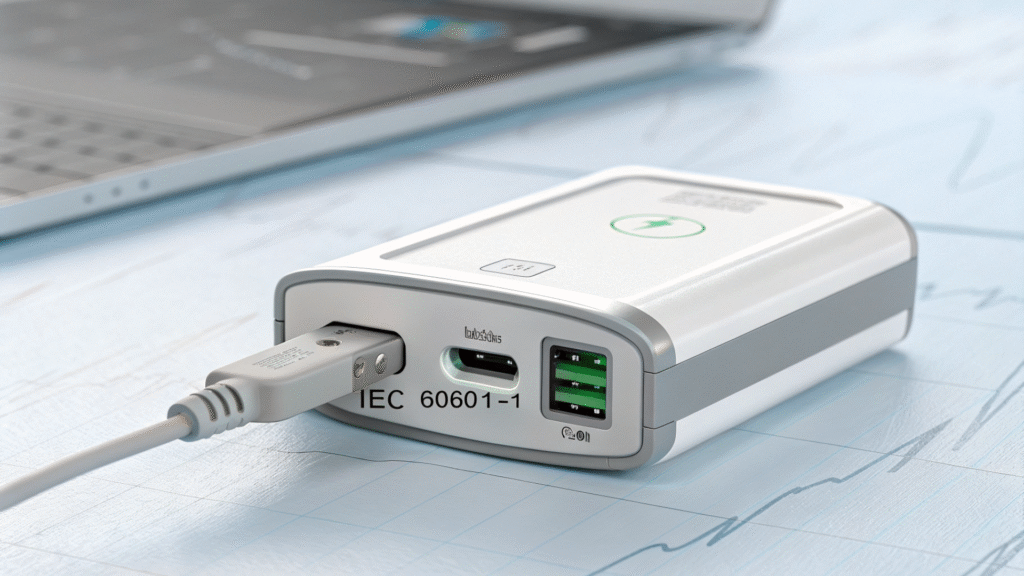

Technical Specifications
Medical-grade power adapters typically operate within a specific voltage and current range tailored to the device they power. For example, a typical remote cardiac monitoring device may require a 5V or 12V output with a current rating of 1-3A. These adapters often include features like overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, and short-circuit protection to safeguard both the device and the patient.
Additionally, they are designed to handle a wide input voltage range (e.g., 100-240V AC) to accommodate global use, making them suitable for patients traveling or living in different regions. Some adapters also support USB-C power delivery, enabling compatibility with modern devices and simplifying the user experience.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
The use of medical-grade power adapters in remote cardiac monitoring is governed by stringent regulatory standards to ensure patient safety and device performance. Key standards include:
- IEC 60601-1: This international standard outlines the general requirements for the safety and essential performance of medical electrical equipment. Medical-grade power adapters must comply with this standard, which includes requirements for electrical safety, mechanical safety, and risk management.
- IEC 60601-1-2: This standard focuses on electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring that medical devices and their power adapters do not interfere with other equipment or suffer from external interference.
- ISO 13485: While not specific to power adapters, this standard governs the quality management systems of medical device manufacturers, ensuring consistent design, production, and testing processes.
- FDA and CE Marking: In the United States, medical-grade power adapters must comply with FDA regulations for medical devices. In Europe, they require CE marking to indicate compliance with EU directives, such as the Medical Device Regulation (MDR).
Manufacturers of medical-grade power adapters must undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to meet these standards. This ensures that the adapters are safe for use in home environments, where patients may lack the technical expertise to troubleshoot issues.
Enabling Remote Cardiac Monitoring: How Power Adapters Make a Difference
The transition from hospital-based to home-based cardiac monitoring relies on the seamless integration of multiple components, including sensors, communication modules, and power supplies. Medical-grade power adapters play a critical role in this ecosystem by addressing several key challenges:
1. Ensuring Continuous Operation
Remote cardiac monitoring devices must operate continuously to capture critical data, such as irregular heart rhythms or sudden cardiac events. Any interruption in power supply could result in missed data, potentially delaying diagnosis or treatment. Medical-grade power adapters provide a stable power source, minimizing the risk of device failure due to power fluctuations or outages. Some adapters also include backup battery charging capabilities, ensuring that devices remain operational during power interruptions.
2. Supporting Patient Mobility
Unlike hospital settings, where patients are often stationary, home-based monitoring requires devices that support an active lifestyle. Medical-grade power adapters are designed to be portable, allowing patients to move freely while wearing or carrying their monitoring devices. For example, a lightweight adapter can be easily plugged into a wall outlet or used with a portable battery pack, enabling patients to travel or engage in daily activities without disruption.
3. Enhancing Data Accuracy
The accuracy of remote cardiac monitoring devices depends on their ability to operate without interference. Medical-grade power adapters are designed to minimize electromagnetic noise, ensuring that the device’s sensors and communication modules function correctly. This is particularly important for devices that transmit data wirelessly to healthcare providers, as any interference could corrupt the data and lead to inaccurate diagnoses.
4. Simplifying Patient Experience
For remote cardiac monitoring to be effective, patients must be able to use the devices with minimal technical expertise. Medical-grade power adapters are designed with user-friendly features, such as plug-and-play connectivity, clear labeling, and compatibility with standard household outlets. This simplifies setup and reduces the likelihood of user errors, making the technology accessible to a broader population, including elderly patients.
5. Supporting Telemedicine Integration
Remote cardiac monitoring is often integrated with telemedicine platforms, allowing healthcare providers to review data in real time and communicate with patients remotely. Medical-grade power adapters ensure that devices remain powered and connected, enabling seamless data transmission to cloud-based platforms or mobile apps. This connectivity is essential for timely interventions, such as adjusting medications or scheduling follow-up appointments.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
The adoption of remote cardiac monitoring, supported by medical-grade power adapters, has significantly improved patient outcomes in several ways:
- Early Detection and Intervention: Continuous monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect abnormalities, such as arrhythmias or heart rate irregularities, in real time. This enables early interventions, reducing the risk of serious complications like stroke or heart attack.
- Reduced Hospitalizations: By monitoring patients at home, healthcare providers can manage chronic conditions more effectively, reducing the need for hospital admissions. Studies have shown that remote cardiac monitoring can reduce hospitalization rates by up to 30% for patients with heart failure.
- Improved Quality of Life: Home-based monitoring allows patients to maintain their independence and engage in daily activities without frequent hospital visits. This is particularly beneficial for elderly patients or those living in rural areas with limited access to healthcare facilities.
- Cost Savings: Remote monitoring reduces healthcare costs by minimizing emergency room visits and hospital stays. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that remote monitoring for heart failure patients resulted in a 20% reduction in healthcare costs over one year.
- Patient Empowerment: By providing patients with access to their heart data, remote monitoring encourages greater engagement in their care. Patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about lifestyle changes or treatment plans.
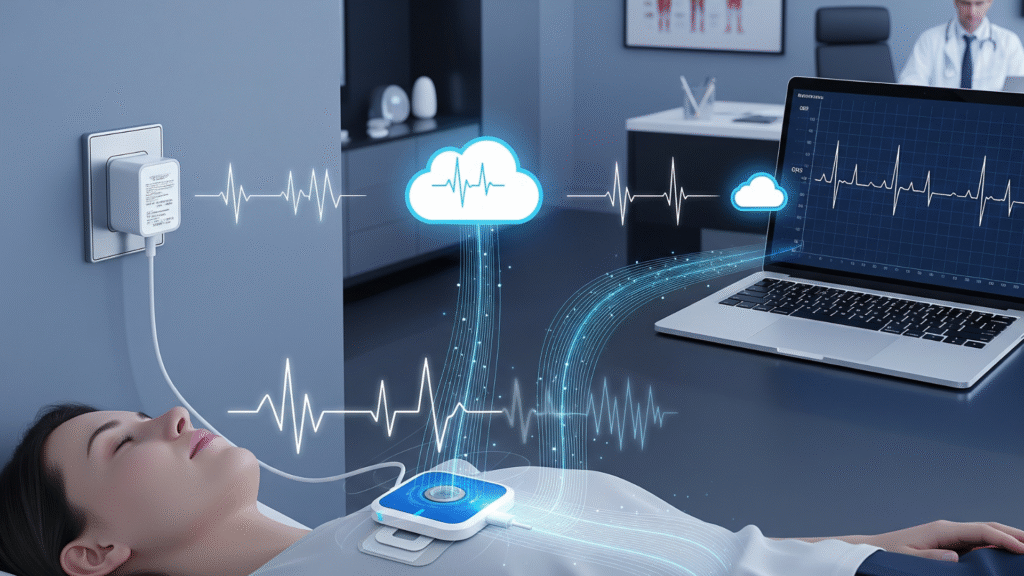

Challenges and Future Directions
While medical-grade power adapters have enabled significant advancements in remote cardiac monitoring, several challenges remain:
- Cost and Accessibility: High-quality medical-grade power adapters can be expensive, potentially limiting access for patients in low-income regions. Manufacturers must balance cost with performance to ensure broader adoption.
- Interoperability: As the number of remote monitoring devices grows, ensuring compatibility between devices and power adapters is critical. Standardized connectors, such as USB-C, can help address this issue.
- Cybersecurity: Remote monitoring devices rely on wireless connectivity, raising concerns about data security and privacy. Power adapters with integrated security features, such as encrypted communication protocols, may become increasingly important.
- Battery Life and Sustainability: While many devices include rechargeable batteries, the longevity and environmental impact of these batteries are concerns. Future power adapters may incorporate advanced energy storage solutions, such as solid-state batteries, to improve sustainability.
Looking ahead, advancements in power adapter technology will further enhance remote cardiac monitoring. For example, wireless power transfer could eliminate the need for physical connectors, improving patient convenience. Additionally, smart power adapters with built-in diagnostics could monitor device performance and alert patients or providers to potential issues, further improving reliability.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case Study 1: Managing Atrial Fibrillation at Home
A 65-year-old patient with atrial fibrillation was prescribed a wearable ECG monitor to track heart rhythm irregularities. The device, powered by a medical-grade adapter, allowed continuous monitoring for 30 days, transmitting data to the patient’s cardiologist. During this period, the device detected several episodes of arrhythmia, enabling the cardiologist to adjust the patient’s medication remotely. The reliable power supply ensured uninterrupted monitoring, preventing a potential stroke.
Case Study 2: Heart Failure Management in Rural Areas
In a rural community with limited access to cardiology services, a heart failure patient used a remote monitoring device to track fluid levels and heart rate. The device’s medical-grade power adapter was designed to operate in unstable power grids, common in rural areas. Over six months, the device helped the patient avoid three hospital admissions by enabling early interventions based on real-time data.
Conclusion
The shift from hospital to home-based cardiac monitoring represents a monumental step forward in healthcare, offering patients greater autonomy and improved outcomes. At the heart of this transformation are medical-grade power adapters, which provide the reliability, safety, and efficiency needed to power life-saving devices. By meeting stringent regulatory standards and addressing the unique challenges of home environments, these adapters enable continuous monitoring, timely interventions, and enhanced quality of life for patients with cardiovascular conditions. As technology continues to evolve, medical-grade power adapters will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of remote healthcare, ensuring that patients can live healthier, more independent lives.