Power adapters have evolved through continuous updates and iterations, resulting in a variety of types and more convenient features. However, this also means consumers must put in more effort to choose the right one. This article will guide you through how to select the ideal power adapter for your device—one that fits perfectly and lasts for years.
What is a power adapter?
A power adapter is generally a converter that transforms 220V AC into DC power for electrical devices. You might wonder—why not use AC power directly? The reason is that most electronic devices cannot operate on AC power. Their internal components, such as integrated circuits and microcontrollers, require a stable voltage and unidirectional current.
AC power fluctuates in voltage and alternates direction periodically, making it unsuitable for such devices. Therefore, a power adapter is needed to provide the stable DC power they require.
Types of power adapters
In general, power adapters can be categorized by structure into linear power adapters, Switching Power Adapters, Wall Plug or Desktop Types, and open-frame or built-in types. When classified by application, they include medical power adapters, LED drivers, ITE (Information Technology Equipment) adapters, PoE (Power over Ethernet) adapters, and home appliance adapters.
Linear power adapters step down voltage through a line-frequency transformer, then rectify and filter it to output DC—these are typically used in older household appliances. Switching power adapters, on the other hand, first convert AC into high-voltage DC, then use a high-frequency switch to control a transformer for voltage reduction. This design makes them the most widely used type of adapter today.
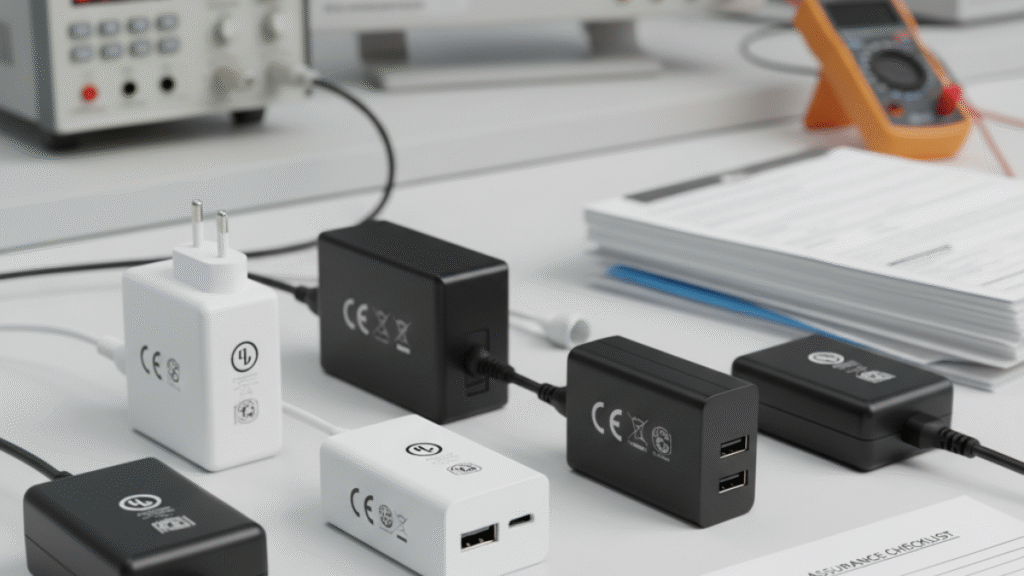
The certifications and safety standards of the power adapter
The first step in choosing a power adapter is to determine which certifications and safety standards your device requires. For example, medical equipment usually needs IEC 60601-1 certification, LED devices require IEC 61347-1, and IT or communication equipment needs IEC 62368-1.
In addition, attention should be paid to the certification requirements of different countries for different types of equipment. Generally, there are safety, EMC (electromagnetic compatibility), and environmental requirements. If the destination country requires such certifications for the equipment itself, the same requirements usually apply to the accompanying power adapter.

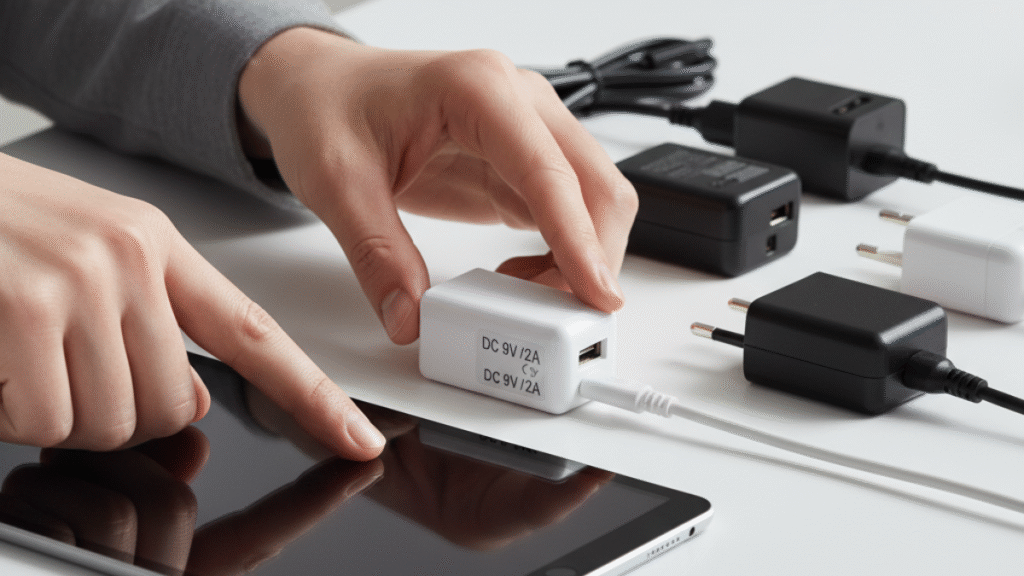
How to choose the appropriate voltage and current of a power adapter
As mentioned above, many electrical devices contain complex integrated circuits and microcontrollers that have very strict requirements for voltage and current. Therefore, when selecting a power adapter, it is important to carefully consider the power rating, meaning the choice of voltage and current.
First, the adapter’s output voltage must match the device’s rated voltage. If the voltage is too high, the device may be damaged; if it is too low, the device may fail to start or operate abnormally.
As for current, the requirement can be more flexible — the adapter’s current can be equal to or greater than the device’s current demand, and the device will still function properly.

AC and DC connectors for a power adapter
When selecting the AC and DC connectors for an adapter, it is important to follow the principles of proper size matching, sufficient electrical capacity, safety compliance, and mechanical reliability.
The connector’s rated current and voltage should exceed the adapter’s maximum output. For example, a 12 V 5 A output should use a DC plug rated for at least 5 A.
The DC plug’s dimensions — inner diameter, outer diameter, and length — must match the device’s socket precisely; otherwise, it may become loose, have poor contact, or fail to insert properly.
Conclusion
Finally, to select the right power adapter, you just need to identify your device type and its specific requirements, and align them with the key points mentioned above. This will allow you to choose the perfect adapter that fits your device.




