In the design and manufacture of medical electrical equipment, patient safety is the highest priority. Power supplies—whether internal modules or external adapters—play a foundational role in ensuring safe, reliable device operation. To safeguard patients, operators, and maintenance personnel, all medical power supplies must comply with the IEC 60601-1 safety standard.
The IEC 60601-1 standard, issued by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), outlines a broad framework of electrical safety, mechanical safety, and environmental protections required for medical electrical equipment. For power supply engineers, compliance with this standard is not optional—it is mandatory for regulatory approval in most global markets.
1. What is IEC 60601-1?
IEC 60601-1 is the international safety standard that governs the design and manufacturing of medical electrical equipment and systems. It ensures that equipment performs safely under normal and fault conditions.
The standard is part of the broader IEC 60601 series, which includes collateral and particular standards for specialized devices. As of 2025, the most recent general standard is IEC 60601-1 Edition 3.2, which includes clarifications and updates to previous versions.
Power supplies—being integral components of virtually all medical devices—must also conform to this standard, even when they are sold as standalone external adapters or embedded modules.
2. Scope and Importance for Power Supplies
IEC 60601-1 applies to:
Internal power supply modules integrated into a medical device (open-frame, enclosed, modular).
External power adapters (wall-mount, desktop) used to power or charge medical devices.
Battery chargers and AC-DC or DC-DC converters that supply energy to applied parts.
Why it matters: Failing to meet IEC 60601-1 standards can lead to:
Regulatory approval delays or rejections (FDA, CE, NMPA).
Legal liability in the event of patient injury.
Product recalls and loss of reputation.
Interference with other medical equipment in critical environments.
3. Core Safety Objectives of IEC 60601-1
IEC 60601-1 addresses multiple categories of safety, including:
Electrical Safety: Protects against shock hazards via insulation, grounding, and current limitation.
Mechanical Safety: Prevents injury from sharp edges, mechanical failures, etc.
Thermal Safety: Prevents burns and overheating.
Fire Safety: Ensures components don’t ignite under fault conditions.
EMC Compatibility: Minimizes electromagnetic interference (covered in 60601-1-2).
For power supplies, electrical insulation, leakage current limitation, and mechanical protection are the most critical elements.
4. Classification of Medical Equipment in IEC 60601-1
IEC 60601-1 defines several key classifications that impact power supply requirements:
a. Class I vs. Class II Equipment
Class I: Has a protective earth (ground) connection. Requires basic insulation + protective earth.
Class II: Double-insulated, no earth connection. Preferred in portable and home-use devices.
b. Applied Part Types
These determine patient leakage current limits and insulation needs:
Type B (Body): Low-risk contact (e.g., hospital beds).
Type BF (Body Floating): Connected to the body (e.g., ultrasound probes).
Type CF (Cardiac Floating): Heart-connected (e.g., ECG electrodes). Requires highest insulation and lowest leakage current.
Power supplies used in BF/CF applications must maintain stricter safety barriers, typically 2 x MOPP.
5. MOPP and MOOP: The Language of Insulation
A cornerstone of IEC 60601-1 is the concept of Means of Protection:
MOPP (Means of Patient Protection): Higher protection level—required when power is connected to applied parts in patient contact.
MOOP (Means of Operator Protection): Lower protection level—sufficient for protecting users but not patients.
To meet 2 x MOPP, a power supply must meet stringent insulation, clearance, creepage, and dielectric strength standards:
| Protection Level | Insulation Type | Creepage Distance | Dielectric Withstand Voltage |
| 1 x MOOP | Basic | 2.5 mm | 1500 VAC |
| 2 x MOOP | Reinforced | 5 mm | 3000 VAC |
| 1 x MOPP | Basic | 4 mm | 1500 VAC |
| 2 x MOPP | Reinforced | 8 mm | 4000 VAC |
For maximum safety and market versatility, many modern medical power supplies are designed to meet 2 x MOPP.
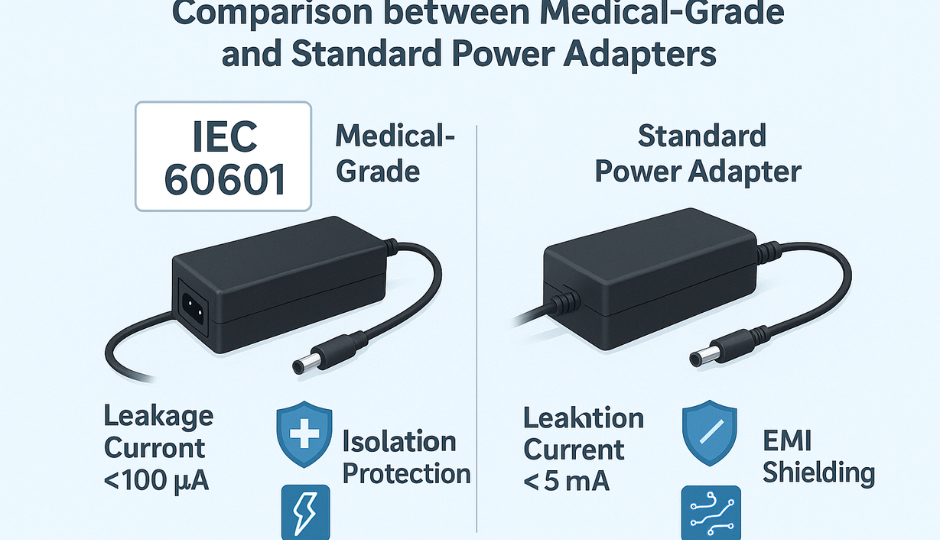
6. Leakage Current Limits for Power Supplies
IEC 60601-1 limits leakage current to protect patients and operators. The most relevant values for power supply designers are:
| Condition | Earth Leakage | Touch Current | Patient Leakage (NC) |
| Normal | ≤ 500 μA | ≤ 100 μA | ≤ 10 μA (CF) |
| Single Fault | ≤ 1000 μA | ≤ 500 μA | ≤ 50 μA (CF) |
Power supply designers must manage Y-capacitor values, shielding, and PCB layout to stay within limits, particularly for Class II and portable equipment.
7. Testing and Documentation Requirements
IEC 60601-1 compliance involves rigorous design validation and documentation, including:
Dielectric Strength (Hi-Pot) Test
Earth Bond Test
Leakage Current Test
Temperature and Overload Protection
Risk Management File (per ISO 14971)
Technical File for CE marking
CB Scheme Certification for global markets
Power supply manufacturers must provide all necessary test reports and documentation. Some suppliers also assist OEMs with pre-compliance testing and integration support.
8. IEC 60601-1 vs IEC 62368-1 and IEC 60950-1
While IEC 62368-1 is replacing IEC 60950-1 in IT and industrial markets, it does not cover medical applications. Medical power supplies must still comply with IEC 60601-1, which includes patient risk management, leakage current, and applied part protection not found in 62368-1.
9. IEC 60601-1-11 for Home Healthcare
As more care shifts to the home, IEC 60601-1-11 becomes crucial. It introduces additional requirements for:
Class II insulation
Ingress protection (e.g., IP21 or higher)
Drop/shock resistance
Accessible labeling and user-friendly operation
Power supplies for home-use devices (e.g., CPAP, nebulizers, breast pumps) must comply with both IEC 60601-1 and 60601-1-11.
10. Choosing a Compliant Medical Power Supply
Medical device developers should choose power supplies that:
Are certified to IEC 60601-1 (Edition 3.1 or 3.2)
Provide 2 x MOPP insulation
Maintain leakage current within CF-level limits
Offer documentation and CB reports
Are manufactured under ISO 13485 quality systems
For example, Quankang offers a wide range of medical-grade AC-DC power adapters and open-frame modules designed and certified to meet IEC 60601-1, including 2 x MOPP and ultra-low leakage current levels suitable for BF and CF-rated devices.
Safety is Engineered Through Standards
IEC 60601-1 is not just a technical guideline—it is a comprehensive safety framework that ensures the protection of patients and caregivers. For power supplies, it influences everything from component selection and PCB layout to insulation design and certification documentation.
Complying with this standard is a fundamental requirement for medical device success in 2025 and beyond. As medical technologies become more portable, connected, and patient-centered, the demands on power supply safety and reliability will only increase.
By understanding and applying IEC 60601-1 standards in the power supply selection and design process, medical OEMs can build safer, globally compliant devices—and build trust with both regulators and end users.




