Introduction: Why Stable Power Matters More Than Ever
Imagine a hospital intensive care unit where patient monitors, ventilators, and infusion pumps operate continuously. In this environment, even the smallest fluctuation in voltage could lead to a false alarm, data corruption, or—in the worst cases—equipment malfunction. Now picture an industrial automation line where precision sensors and controllers work in perfect harmony; a sudden power spike could halt the production process entirely, leading to costly downtime.
These scenarios are not far-fetched—they are real-world examples of why regulated power supplies are critical. In today’s interconnected world, where electronics drive industries from healthcare to aerospace, delivering stable, clean power is not a luxury; it is an operational necessity.
At the heart of this requirement lies the regulated power supply—a device designed to provide a constant output voltage regardless of changes in input voltage or load conditions. Whether you are working on medical diagnostic equipment, industrial robotics, or consumer electronics, a regulated power supply ensures that your system operates within its intended electrical parameters, safeguarding both performance and longevity.
What is a Regulated Power Supply?
A regulated power supply is an electronic device that delivers a stable voltage output to a load, even when the input voltage or load current changes. The main purpose of voltage regulation is to protect sensitive components from electrical fluctuations that could cause malfunctions or permanent damage.
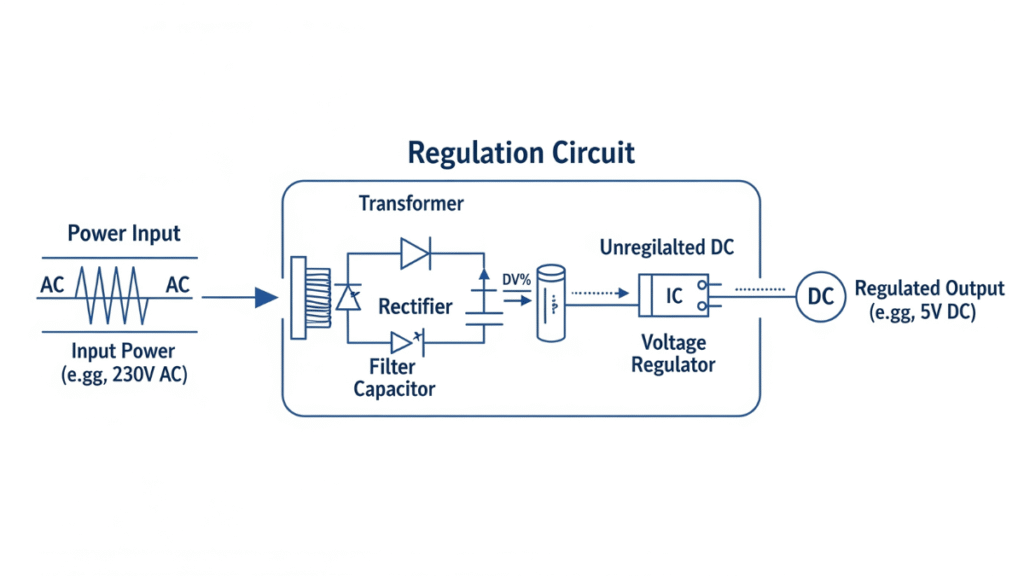
How It Works
Regulated power supplies typically use feedback control mechanisms. The device continuously monitors the output voltage and compares it to a reference voltage. If the output drifts from the desired level, the regulation circuitry makes real-time adjustments to bring it back in line.
This process ensures:
- Voltage stability: Preventing over-voltage or under-voltage conditions.
- Noise suppression: Reducing electrical noise and ripple for sensitive applications.
- Load adaptability: Maintaining voltage regardless of changes in connected devices.
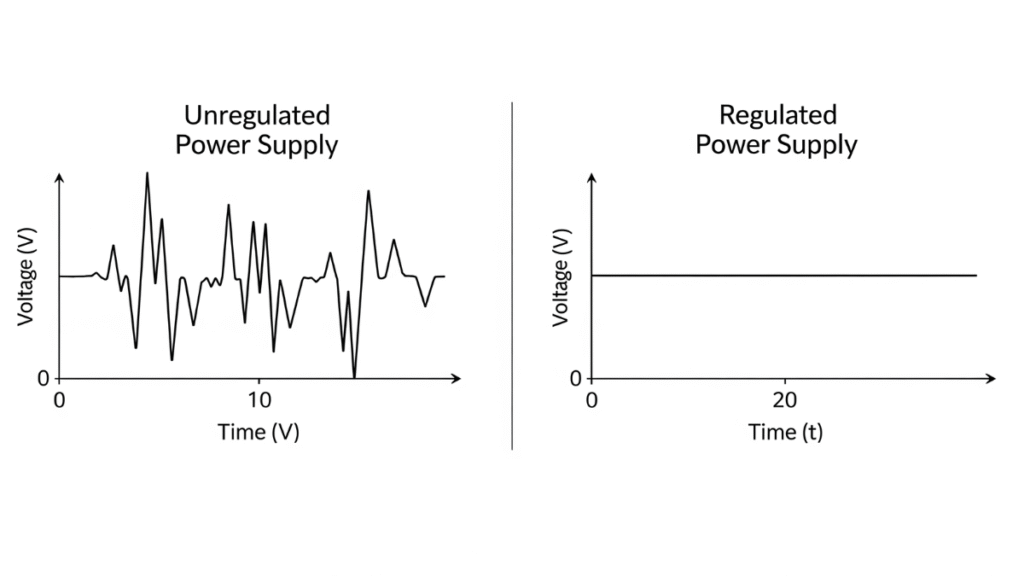
Unregulated vs. Regulated Power Supplies
To understand why regulated power is so valuable, let’s compare it with unregulated power supplies.
| Feature | Unregulated Power Supply | Regulated Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Output voltage stability | Varies with load and input voltage | Maintains constant voltage |
| Noise filtering | Minimal | Strong noise suppression |
| Efficiency | Often higher at low loads | Consistent performance across loads |
| Suitable applications | Low-cost devices, non-critical loads | Sensitive electronics, precision instruments |
While unregulated supplies may be acceptable for simple devices like basic LED lighting, they are unsuitable for precision electronics such as medical diagnostic machines, laboratory equipment, and advanced communication systems.
Types of Regulated Power Supplies
1. Linear Regulated Power Supplies
Principle of Operation
A linear regulated power supply utilizes linear regulators—often based on semiconductor devices, such as transistors—to drop excess voltage and maintain a steady output. The regulator dissipates extra voltage as heat, ensuring smooth voltage output.
Advantages
- Low noise and ripple
- Fast transient response
- Simple design with fewer components
Disadvantages
- Lower efficiency (often 30–60%)
- Heat dissipation requires larger heatsinks
- Not ideal for high-power applications
Applications
- Audio equipment (to avoid audible noise)
- Laboratory instruments
- Low-power analog circuits
2. Switching Regulated Power Supplies
Principle of Operation
Switching regulated power supplies use high-frequency switching transistors and energy storage components (inductors, capacitors) to regulate output voltage. Instead of dissipating extra voltage as heat, they rapidly switch the input on and off, adjusting duty cycles to control the output.
Advantages
- High efficiency (up to 90% or more)
- Smaller size and weight due to reduced heat generation
- Wide input voltage range
Disadvantages
- More complex design
- Potential for electromagnetic interference (EMI)
- Requires filtering to reduce output noise
Applications
- Industrial machinery
- Medical devices with high power demands
- Portable electronics and IoT devices
Why Choose a Regulated Power Supply?
- Protecting Sensitive Devices.:Fluctuations in voltage can cause data errors, overheating, and even component failure. Regulated power ensures consistent operation, especially for ICs, microcontrollers, and precision analog circuits.
- Improving Accuracy and Performance: In measurement devices—like digital scales, ECG monitors, or oscilloscopes—voltage stability is critical for accurate readings.
- Prolonging Equipment Lifespan: Stable voltage reduces electrical stress, extending the operational life of semiconductors, capacitors, and other sensitive parts.
- Meeting Safety and Compliance Standards: Many industries require compliance with strict electrical and EMC regulations. Using a regulated power supply simplifies the certification process.
Industry Applications of Regulated Power Supplies
Medical Equipment
From ultrasound machines to portable oxygen concentrators, regulated power supplies are essential in meeting IEC60601 medical safety standards. Any power disturbance in such equipment can directly impact patient safety.
Industrial Automation
PLC systems, robotic arms, and conveyor belt controls demand high reliability. Even a brief power fluctuation could halt production, causing hours of downtime.
Telecommunications
Base stations, data servers, and networking devices require stable voltages to prevent dropped connections and data corruption.
Consumer Electronics
Devices like gaming consoles, 3D printers, and smart home systems require consistent power for optimal user experience.
How to Select the Right Regulated Power Supply
- Determine Voltage and Current Requirements: Match your supply output to your device’s operating needs.
- Consider the Load Type: Resistive, capacitive, and inductive loads all have different power characteristics.
- Evaluate Efficiency and Heat Management: Higher efficiency means less wasted energy and smaller cooling requirements.
- Check Safety and Certification Requirements: For global markets, ensure compliance with UL, CE, FCC, or IEC standards.
- Plan for Future Scalability: If your device’s power requirements might increase, choose a power supply with some margin.
Quankang’s Regulated Power Solutions
At Guangzhou Quankang Technology Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-quality regulated power supplies and adapters for medical, industrial, and consumer applications. Our products feature:
- Output power from 5W to 150W
- Compliance with IEC60601, DOE VI, UL, CE
- Low ripple and noise for sensitive equipment
- Customizable solutions to match your exact specifications
Whether you need a compact medical-grade adapter or a robust industrial power module, we deliver reliability and performance in every product.
Conclusion
In the world of modern electronics, where precision, safety, and efficiency are paramount, regulated power supplies are the unsung heroes. They protect sensitive devices, improve performance, and extend product lifespan—while ensuring compliance with strict industry standards.
Investing in a high-quality regulated power supply is not just a technical choice—it’s a strategic decision for product reliability and customer satisfaction.




