Introduction
Power adapters have become an inseparable part of modern life, enabling the safe and efficient use of countless electronic devices. From charging a smartphone to powering a wireless router or supplying critical energy to medical diagnostic equipment, adapters serve as the bridge between unstable AC mains and the delicate electronics that rely on stable DC power. While the external casing of an adapter gives the impression of a simple device, inside lies a carefully engineered network of components, each ensuring safety, compliance, and performance. Among these, capacitors play one of the most vital roles. Power supply capacitors are responsible for smoothing, filtering, and stabilizing voltage and current, directly influencing the reliability and longevity of the entire adapter.
This article explores the essential role of capacitors in power supplies, with a focus on adapters used in consumer electronics, communication devices, and medical equipment. It examines the working principles, different capacitor types, their placement in circuits, design challenges, reliability issues, international standards, and evolving trends in capacitor technology.
The Basic Principle of Power Supply Capacitors
Capacitors are passive components designed to store and release electrical energy. Their structure consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating dielectric material. When voltage is applied, an electric field develops across the dielectric, and charges accumulate on the plates. This ability to temporarily hold energy allows capacitors to smooth voltage fluctuations, absorb spikes, and release stored energy when demand suddenly increases.
In power supply design, capacitors are crucial for transforming alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). After rectification, the voltage waveform still contains ripples. Capacitors at the input stage store energy during voltage peaks and release it during valleys, reducing these ripples and providing a more stable DC signal. Beyond smoothing, capacitors also serve as filters for high-frequency noise, protect circuits from transients, and ensure the stable operation of sensitive electronic loads.
The effectiveness of a capacitor depends on parameters such as:
- Capacitance (μF or F): Determines how much charge can be stored.
- Rated Voltage: The maximum voltage the capacitor can handle without breakdown.
- ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance): Affects efficiency and heat generation.
- Temperature Rating: Defines the operating range and influences the lifetime.
- Lifetime Expectancy: Critical in applications where durability is essential.
Placement and Functions of Capacitors in Power Adapters
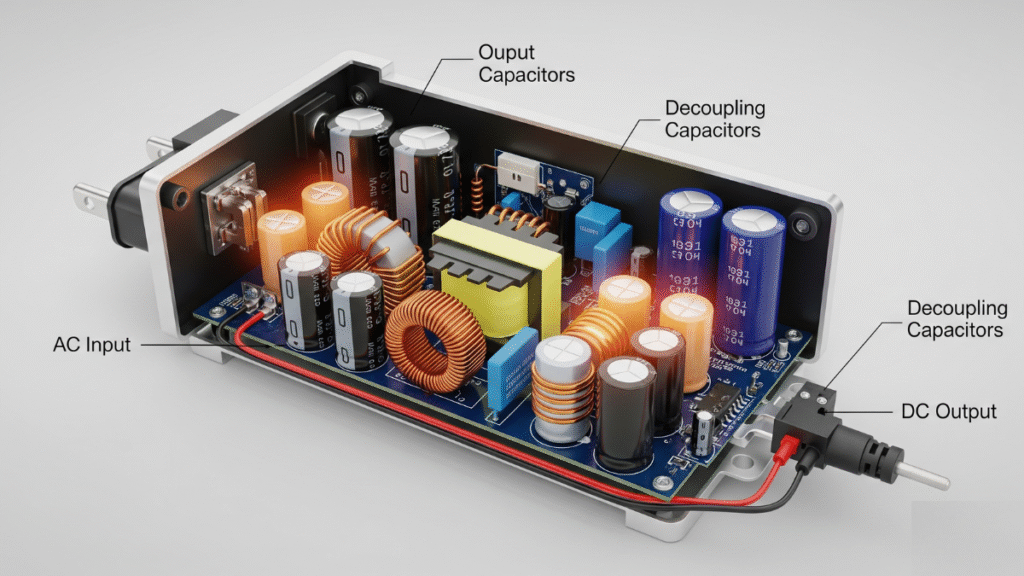
In a power adapter, capacitors are strategically placed at multiple points in the circuit, each serving a specific role:
- Input Capacitors: Positioned after rectification, they stabilize the DC bus, reduce voltage ripple, and help achieve compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations.
- Output Capacitors: Found at the DC output stage, they ensure that the voltage supplied to the device remains smooth, stable, and within defined tolerance limits. These capacitors also reduce ripple voltage, which is critical for devices such as smartphones or medical monitors that require clean signals.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Placed near integrated circuits or sensitive components, they suppress high-frequency noise and improve transient response.
- Snubber Capacitors: Used across switching devices to absorb voltage spikes generated by switching transients.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Capacitors: Designed to minimize conducted and radiated interference, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Without capacitors, a power adapter would be unable to meet even the most basic requirements of modern electronics. Voltage would fluctuate, noise would interfere with operation, and devices could malfunction or even fail permanently.
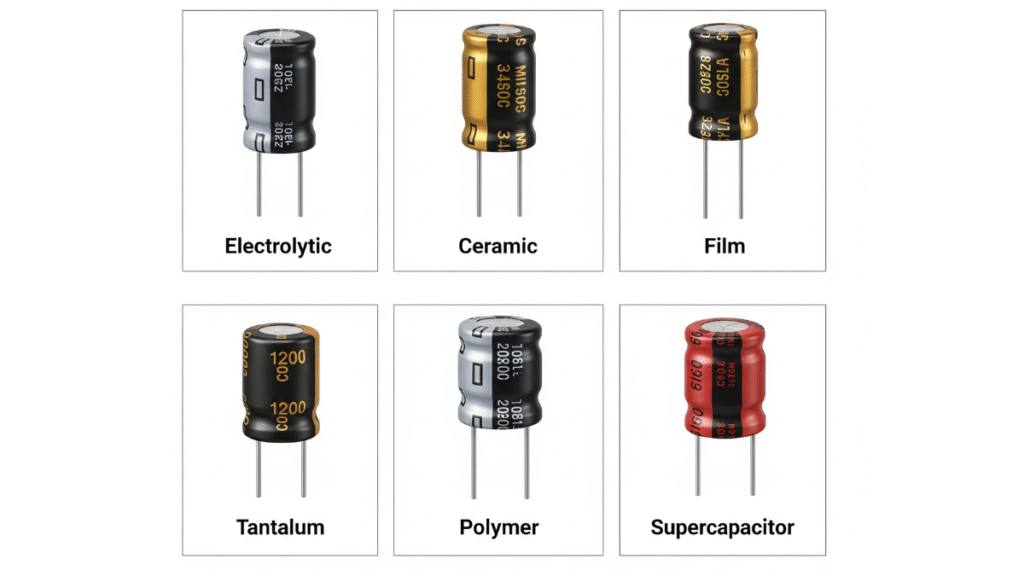
Types of Capacitors Used in Power Supplies
The wide range of functions performed by capacitors in adapters necessitates the use of different capacitor technologies. Each type offers unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations.
1. Electrolytic Capacitors Electrolytic capacitors, particularly aluminum electrolytics, are the most common in power supplies due to their high capacitance values. They are ideal for bulk energy storage and smoothing functions, especially at the input and output stages. However, their disadvantages include relatively short lifespans, sensitivity to high temperatures, and gradual performance degradation over time.
2. Ceramic Capacitors Ceramic capacitors are widely used for decoupling and bypassing applications. They feature low ESR, excellent high-frequency performance, and long lifespans. Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) have become increasingly common due to their small size and ability to operate effectively at high frequencies.
3. Film Capacitors Film capacitors use plastic films as dielectrics and are known for their high stability, low losses, and excellent reliability. They are often used in EMI suppression and applications requiring precise filtering.
4. Tantalum Capacitors Tantalum capacitors offer compact size and stable performance with lower ESR compared to aluminum electrolytics. They are more expensive and must be carefully protected against overvoltage, but they provide excellent reliability in compact adapters.
5. Solid-State and Polymer Capacitors Solid-state capacitors use conductive polymers as electrolytes, offering superior stability, lower ESR, and longer lifetimes compared to traditional electrolytics. They are increasingly used in high-performance adapters where reliability is critical.
6. Supercapacitors Although not common in everyday adapters, supercapacitors are finding niche applications in systems requiring large bursts of energy or backup power. They combine high capacitance with fast charging and discharging capabilities.

Capacitor Selection and Its Impact on Adapter Performance
The selection of capacitors directly affects an adapter’s performance, safety, and longevity. For consumer electronics, the challenge lies in balancing cost, size, and efficiency. In communication equipment, noise suppression and stable output are critical for uninterrupted connectivity. For medical devices, capacitors must meet stringent safety and reliability standards, as performance failure can directly impact patient health.
- Efficiency: Capacitors with low ESR minimize power losses and reduce heat generation, improving overall efficiency.
- Ripple Reduction: Adequate capacitance ensures minimal ripple, protecting sensitive electronics.
- Temperature Tolerance: High-quality capacitors rated for higher temperatures extend lifespan.
- Compliance: Correct selection ensures the adapter complies with international standards such as IEC 60601 for medical applications or IEC 62368 for consumer electronics.
A poorly chosen capacitor can lead to instability, device malfunction, overheating, or premature failure. In practice, capacitor quality often defines the overall lifetime of a power adapter.
Common Failures and Reliability Issues
Capacitors, especially electrolytic types, are among the most failure-prone components in a power supply. Common issues include:
- Electrolyte Drying: Leads to reduced capacitance and increased ESR.
- Leakage and Bulging: Caused by chemical degradation under heat and stress.
- Dielectric Breakdown: Triggered by voltage surges or manufacturing defects.
- Thermal Stress: High temperatures accelerate aging and shorten lifespan.
The consequences of capacitor failure vary depending on the application. In consumer electronics, it may result in an unusable charger. In communication equipment, it could cause intermittent connectivity or system resets. In medical devices, capacitor failure can pose safety risks and disrupt critical monitoring functions.
Manufacturers mitigate these risks by utilizing high-temperature-rated capacitors, implementing derating practices, and designing efficient thermal management systems.

Applications of Capacitors in Different Fields
Consumer Electronics Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and gaming consoles all rely on adapters with well-designed capacitor networks. Output capacitors ensure a clean DC voltage for charging batteries, while input capacitors protect against mains instability. The growing demand for compact chargers, including USB-C Power Delivery adapters, pushes capacitor design toward higher density and improved thermal performance.
Communication Equipment Routers, modems, and small cell base stations depend on stable power to maintain uninterrupted connectivity. Capacitors play a key role in filtering voltage fluctuations and suppressing high-frequency noise that could interfere with signal integrity. The use of MLCCs and solid capacitors ensures reliability and reduced downtime in communication networks.
Medical Devices In medical equipment such as patient monitors, diagnostic imaging systems, and portable therapy devices, capacitors are crucial for both safety and performance. They must comply with IEC 60601 standards, ensuring low leakage currents, safe isolation, and long-term reliability. Failures are unacceptable, as they can directly impact patient health and safety. Capacitors in these applications are carefully selected for stability, durability, and compliance with strict international regulations.
Standards and Compliance
Capacitor selection in power adapters is influenced by international safety and performance standards.
- IEC 60601: Governs medical electrical equipment, requiring capacitors with high reliability and low leakage currents.
- IEC 62368: Applies to audio, video, and ICT equipment, ensuring safe capacitor performance in consumer electronics and communication devices.
- RoHS and REACH: Restrict the use of hazardous materials, shaping the choice of capacitor materials.
- UL Certification: Ensures compliance with North American safety standards.
Adherence to these standards guarantees not only safe operation but also market acceptance in different regions.
Trends and Future Developments
Capacitor technology continues to evolve in response to the demand for smaller, more efficient, and environmentally friendly adapters. Key trends include:
- Solid-State Capacitors: Offering longer lifespans and higher stability, they are increasingly replacing electrolytics in critical designs.
- Miniaturization: Driven by compact USB-C and GaN-based adapters, requiring capacitors with higher density.
- High-Temperature Operation: Capacitors designed for 125°C or higher to meet demanding conditions.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Development of capacitors free from hazardous substances in compliance with global regulations.
- Integration with Smart Power Systems: Capacitors are being optimized for adapters that include intelligent control and monitoring features.
As devices become more power-hungry yet compact, capacitor innovation will remain central to the development of next-generation power adapters.
Conclusion
Capacitors are more than just passive elements inside a power adapter. They are the backbone of reliable energy conversion, ensuring that electronic devices operate safely, efficiently, and without interruption. Whether it is a smartphone charger, a wireless router adapter, or a power supply for a life-saving medical device, capacitors define performance, durability, and compliance with international standards.
Understanding the types, functions, and reliability of capacitors allows designers to create adapters that meet the growing demands of modern electronics. As capacitor technologies evolve toward solid-state, miniaturized, and environmentally sustainable solutions, power adapters will continue to advance in efficiency, safety, and functionality.