In the fast-evolving medical device industry, power adapters play a critical role—not just in supplying electricity, but in ensuring the safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance of the entire system. A medical grade power adapter isn’t simply a well-designed power brick; it must undergo rigorous certification to meet the stringent requirements of the healthcare sector.
Whether powering life-support equipment in hospitals or portable diagnostic devices used at home, medical-grade adapters must meet international standards that protect patients and ensure device reliability in complex and often high-risk environments.
1. IEC 60601-1: The Cornerstone of Medical Safety
What it is:
IEC 60601-1 is the primary international standard for the safety and essential performance of medical electrical equipment. It is mandatory for any adapter used in medical devices sold globally.
Key Requirements for Power Adapters:
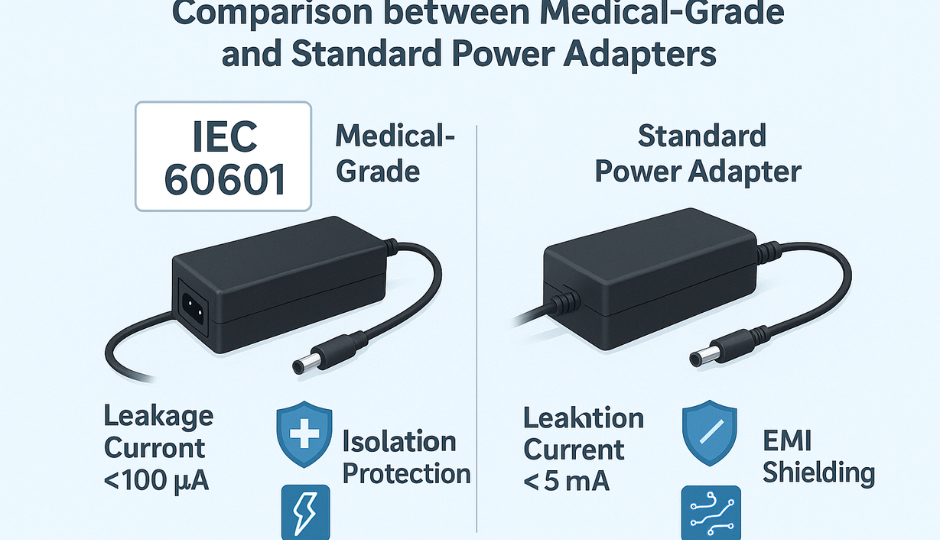
Electrical isolation between input/output (typically 4000 VAC)
Leakage current within ultra-low thresholds (e.g., ≤10μA for CF equipment)
Use of 2 x MOPP (Means of Patient Protection) insulation
Risk management according to ISO 14971
Physical layout that ensures mechanical safety (e.g., spacing, grounding)
Latest Edition:
IEC 60601-1 Edition 3.2 (2020) is the current version and includes updated guidance on insulation coordination and test procedures.
Why it matters:
Adapters without IEC 60601-1 cannot be used in medical devices in most markets. Certification to this standard is essential for CE marking in the EU, FDA approval in the U.S., and global acceptance via the CB Scheme.
2. IEC 60601-1-2: Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
What it is:
A collateral standard in the 60601 series, IEC 60601-1-2 specifies limits on electromagnetic interference (EMI) and susceptibility for medical devices.
Why it matters:
Medical environments contain many sensitive electronic devices. A power adapter must not:
Emit excessive EMI that could interfere with nearby equipment
Be overly susceptible to disturbances (e.g., from defibrillators, cell phones)
Compliance Methods:
Conducted/radiated emissions testing (CISPR 11, Group 1 Class B)
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), EFT, surge immunity testing
RF immunity tests (80 MHz – 2.7 GHz)
Implication:
Adapters certified to IEC 60601-1-2 are proven to perform safely and reliably in hospital and clinical settings, where electromagnetic integrity is critical.
3. IEC 60601-1-11: Home Healthcare Standard
What it is:
This standard applies to medical equipment used outside professional healthcare facilities, such as in homes, care centers, or remote clinics.
Power Adapter Requirements:
Class II insulation (no earth grounding required)
Protection against ingress (minimum IP21)
Mechanical stability (e.g., drop resistance)
Simple usability and safe labeling
Why it matters:
With the rise of telehealth, wearable diagnostics, and home-use therapy devices, adapters must be designed for less controlled environments.
Examples of applicable devices:
CPAP machines
Electric breast pumps
Pulse oximeters
Personal TENS units
4. UL 60601-1 and ANSI/AAMI ES60601-1 (U.S. Market)
What it is:
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) provides North American certification to demonstrate that medical adapters meet NFPA electrical safety requirements.
UL 60601-1 and ANSI/AAMI ES60601-1 are the U.S. harmonized versions of the IEC 60601-1 standard.
Required for devices marketed in the United States and Canada (via cUL mark).
Why it matters:
UL listing increases trust among buyers, regulators, and hospital procurement teams, and is often a prerequisite for FDA approval.
5. CB Scheme Certification
What it is:
The CB Scheme is an international system for mutual recognition of electrical product safety testing.
What it includes:
A single set of test reports accepted in 50+ countries
Covers IEC 60601-1 and other applicable standards
Why it matters:
A power adapter with a CB Test Certificate is far easier to bring to market across Europe, Asia, Latin America, and Africa, reducing time and cost for regulatory approval.
6. CE Marking (European Union)
What it is:
CE marking indicates that a medical adapter complies with relevant EU directives and can be sold within the European Economic Area.
Key Directives for Medical Adapters:
MDR (Medical Device Regulation) 2017/745
Low Voltage Directive (LVD)
EMC Directive
RoHS Directive
Why it matters:
CE marking is legally required to sell any medical device in Europe. Power adapters used in those devices must comply as part of the system.
7. FCC Part 15 (United States)
What it is:
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Part 15 regulates electromagnetic interference from electronic devices.
What it tests:
Conducted and radiated emissions
Unintentional RF transmission
Why it matters:
Medical adapters used in the U.S. must meet FCC Part 15 to avoid interference with wireless medical and communication equipment.
8. ISO 13485: Medical Quality Management Systems
What it is:
ISO 13485 is the international standard for quality management in medical device manufacturing.
Power Adapter Manufacturer Requirements:
Documented risk management and design control
Traceability of components and production batches
Change notification and corrective action systems
Regulatory compliance tracking
Why it matters:
Choosing an adapter manufacturer certified to ISO 13485 ensures that products are developed in a controlled, regulatory-aligned process, critical for audit readiness and long-term reliability.
9. RoHS and REACH Compliance
What they are:
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Limits lead, mercury, cadmium, and other toxic substances in electronics
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Ensures safe use of chemical substances
Why they matter:
Medical power adapters must comply with these regulations to be sold in the EU and many other markets. Non-compliant units risk seizure at customs or rejection during product audits.
10. Labeling and Traceability Standards
Certified medical adapters must include:
Clear identification (model number, input/output, date code)
Certification logos (UL, CE, CB, FCC)
Country of origin
Compliance with UDI (Unique Device Identification) when required
Proper labeling is often audited during device certification and market surveillance.
Conclusion: Certification Defines Trust and Safety
In the medical world, a power adapter is more than just a component—it’s a critical link in the safety chain between the wall socket and the patient. Without proper certification, even the best-engineered device may be denied market access, face costly delays, or—worse—put patients at risk.
When choosing a medical grade power adapter, ensure it is certified to:
IEC 60601-1 (and -1-2, -1-11 if applicable)
UL/ES60601-1 and FCC (for North America)
CE and CB Scheme (for Europe and global use)
RoHS, REACH, and ISO 13485 (for environmental and process quality)
Quankang, as a trusted medical power supply manufacturer, offers a full range of Class II, IEC 60601-1 certified power adapters, with ultra-low leakage current, 2 x MOPP insulation, and full EMC and home-healthcare compliance. With ISO 13485-certified production and global safety approvals (CE, CB, UL, FCC), Quankang adapters ensure your medical device is not only powered—but fully protected and globally ready.