Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, electronic devices have become an integral part of everyday life, encompassing a wide range of applications, from household appliances and office equipment to industrial machines and medical devices. At the core of every device’s functionality lies a reliable power supply system, ensuring that the device operates safely and efficiently. Among the critical components of this system are AC power connectors, which act as the physical interface between the electrical grid and the equipment. For manufacturers and users of power adapters, selecting the right AC power connector type is not merely a matter of convenience—it is a vital decision that impacts safety, compatibility, and long-term reliability.
This article offers an in-depth examination of AC power connector types, their history, standards, applications, and their relationship with modern power adapters. By examining global variations, safety regulations, and practical considerations, we aim to provide a comprehensive resource that helps businesses and professionals choose the correct connector for their specific needs.
The Role of AC Power Connectors in Electrical Systems
AC power connectors are more than just physical plugs; they are the gateway through which alternating current is delivered from the mains supply to electronic devices. Their design ensures not only secure electrical contact but also user safety. An inappropriate connector can result in inefficient power delivery, overheating, or even severe electrical hazards.
For power adapters, especially those used in consumer electronics, medical equipment, and industrial systems, AC power connectors must balance compact design, safety compliance, and durability. Since power adapters serve as intermediaries between the AC mains and the device, their connector type must align with both international standards and end-user convenience.
Historical Evolution of AC Power Connectors
The origins of AC connectors date back to the early 20th century, when electricity was becoming widespread. In the beginning, manufacturers often developed proprietary connectors, leading to a lack of uniformity and significant safety concerns. Over time, as international trade expanded, governments and standardization bodies sought to create unified designs.
By the mid-20th century, different regions began adopting distinct standards. For example, North America developed the NEMA series connectors, while Europe adopted CEE 7/7 plugs, and the UK introduced its own BS 1363 design. Although global harmonization remains incomplete, the drive for standardized connectors has dramatically reduced accidents and improved cross-border compatibility.
Key Categories of AC Power Connectors
Today, AC power connectors are divided into several categories, each serving unique applications:
NEMA Connectors
Widely used in North America, NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) connectors come in various configurations, such as NEMA 1-15 (two-prong, ungrounded) and NEMA 5-15 (three-prong, grounded). Higher current versions, like NEMA 6-15, are used in industrial and commercial environments.
IEC Connectors
Globally recognized, IEC 60320 connectors are commonly found in power adapters, computers, and medical devices. Their standardized inlet and outlet system ensures interchangeability and safety. Types include:
- C5/C6 (“Mickey Mouse” or cloverleaf) is used for compact laptops and adapters.
- C7/C8 (figure-eight) for smaller devices.
- C13/C14 for desktop computers and medical-grade adapters.
- C19/C20 for high-power equipment.
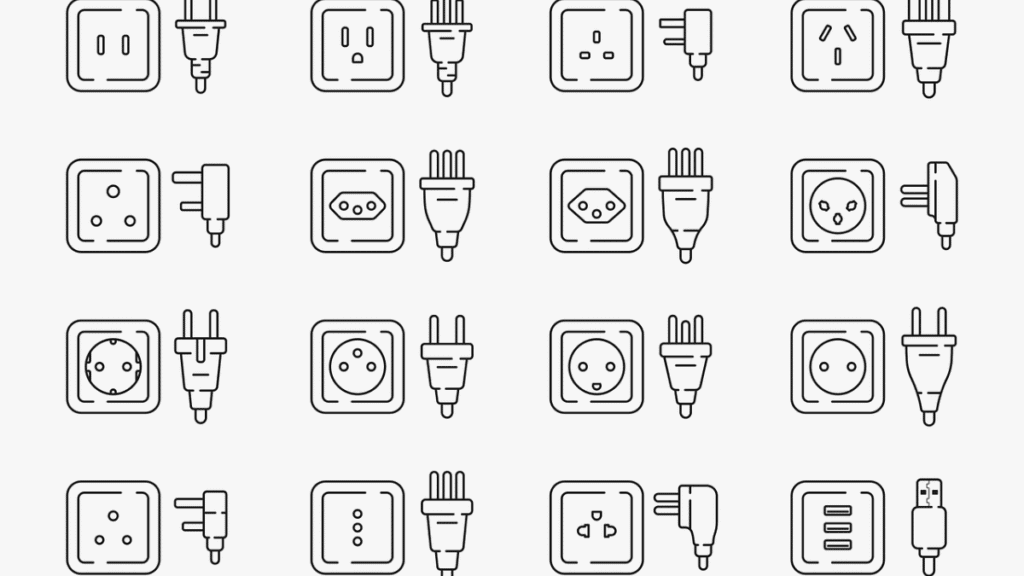
Regional Connectors
Different regions have unique plug types, such as:
- Type G (UK, BS 1363) with fuse protection.
- Type C (Europlug) is widely compatible in Europe.
- Type I (Australia, China) with angled pins.
- Type A/B (Japan, USA), similar to NEMA but with slight dimensional differences.
Specialized Connectors
For environments requiring durability and water resistance, connectors with IP-rated enclosures are employed. In medical applications, IEC 60601-1 compliant connectors are essential, ensuring reduced leakage current and patient safety.
AC Power Connectors and Power Adapters
Power adapters are a bridge between the high-voltage AC mains and the low-voltage DC output required by most electronics. The AC power connector on the input side determines how easily the adapter integrates into the user’s environment.
- Medical Adapters: Require IEC 60320 C13 or C14 connectors to meet safety compliance.
- Consumer Electronics Adapters: Often use figure-eight (C7/C8) or cloverleaf (C5/C6) connectors for portability.
- Industrial Adapters: Use ruggedized connectors capable of handling higher currents.
Selecting the right connector ensures not only regulatory compliance but also market adaptability, especially for manufacturers selling products internationally.

Safety Standards and Compliance
Safety is paramount in AC power connectors. Key standards include:
- IEC 60320 (international standard for appliance couplers).
- UL 498 (North American standard for attachment plugs and receptacles).
- BS 1363 (UK standard requiring fuse protection).
- IEC 60601-1 (medical device safety standard).
For power adapter manufacturers, compliance ensures smooth entry into regulated markets, reduces liability risks, and builds customer trust. Non-compliant connectors may face import bans, recalls, or legal consequences.
Global Variations and Compatibility Challenges
With over a dozen plug types used worldwide, international compatibility remains a challenge. A laptop adapter sold in the US may require a NEMA connector, while the same model in Europe must ship with a CEE 7/7 plug. Manufacturers often solve this by:
- Modular power cords with interchangeable connectors.
- Universal adapters supporting multiple plug types.
- Region-specific product lines, though, increase production costs.
For global manufacturers, striking a balance between logistical efficiency and local compliance is crucial.

Materials, Durability, and Performance
Connector performance depends heavily on its material composition. High-quality copper or brass conductors ensure efficient current flow, while durable plastics or thermoset materials provide insulation and fire resistance. Advanced designs may incorporate nickel plating to resist corrosion.
For power adapters used in medical or industrial environments, connectors must withstand frequent insertions, high humidity, and thermal stress. Choosing the right material can significantly extend the lifespan of both the connector and the adapter.
Trends in AC Power Connector Development
The rise of compact devices and energy efficiency has influenced connector design. Key trends include:
- Miniaturization: Slimmer connectors for portable adapters.
- Eco-friendly materials: Compliance with RoHS and environmental standards.
- Smart connectors: Integration with monitoring systems for predictive maintenance.
- Universal compatibility: Push toward harmonized standards to reduce complexity.
Practical Considerations for Manufacturers and Users
When selecting an AC power connector, both manufacturers and end-users should evaluate:
- Voltage and current requirements of the device.
- Regulatory compliance in target markets.
- Durability for frequent plug-in cycles.
- Environmental resistance (IP rating for moisture and dust).
- Ergonomics and portability for consumer devices.
For power adapter companies, this choice also reflects branding and market positioning. A poorly chosen connector may reduce usability, while a well-designed connector enhances customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
AC power connectors may seem like small components, but they play an outsized role in the safe and efficient operation of electronic devices. For manufacturers of power adapters, understanding connector types, standards, and applications is critical for designing products that meet both regulatory requirements and user expectations.
From the widely used NEMA connectors in North America to the IEC couplers found in global devices, each connector type reflects a balance of history, engineering, and safety considerations. As technology evolves and the demand for universal solutions grows, the future of AC power connectors will likely involve greater standardization, improved safety, and enhanced adaptability across international markets.
By making informed decisions about connector types, manufacturers can not only ensure compliance and reliability but also strengthen their competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving electronics industry.